You are subscribed to updates from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
CDC H1N1 Flu Website Situation Update, January 10, 2010
It's National Influenza Vaccination Week!
 January 10-16 is National Influenza Vaccination Week (NIVW). NIVW was established to highlight the importance of continuing influenza vaccination, as well as fostering greater use of flu vaccine after
the
holiday season.
January 10-16 is National Influenza Vaccination Week (NIVW). NIVW was established to highlight the importance of continuing influenza vaccination, as well as fostering greater use of flu vaccine after
the
holiday season.
Since 2009 H1N1 disease is likely to continue, NIVW is an important opportunity to maintain or increase the number of people who get the 2009 H1N1 vaccine at a time when demand for vaccine usually drops significantly. Though this has been an unprecedented year in terms of the number of people who have received flu vaccinations, most people still have not gotten the 2009 H1N1 vaccine - there is still room for improvement among every age and risk group. Influenza is unpredictable and we do not know the likelihood of a future wave of 2009 H1N1 influenza, but we do know that vaccination is the single best way to reduce the health impact of influenza.
To learn more about NIVW, visit the NIVW website.
Key Flu Indicators
Each week CDC analyzes information about influenza disease activity in the United States and publishes findings of key flu indicators in a report called FluView. During the week of December 27, 2009-January 2, 2010, most key indicators declined compared to the previous week. Below is a summary of the most recent key indicators:
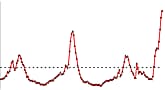
- Visits to doctors for influenza-like illness (ILI) nationally decreased this week over last week. Visits to doctors for ILI also are examined by region. ILI increased in 4 regions, but decreased in 6 regions of the country.
- Overall hospitalization rates for this season were unchanged from the previous week in all age groups.
- The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) based on the 122 Cities Report decreased over the previous week and is back below the epidemic threshold. (The epidemic threshold is the point at which the observed proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia or influenza is significantly higher than would be expected at that time of the year in the absence of substantial influenza-related mortality.) In addition, another four flu-related pediatric deaths were reported this week: all four of these deaths were associated with laboratory confirmed 2009 H1N1. Since April 2009, CDC has received reports of 293 laboratory-confirmed pediatric deaths: 248 due to 2009 H1N1, 43 pediatric deaths that were laboratory confirmed as influenza, but the flu virus subtype was not determined, and two pediatric deaths that were associated with seasonal influenza viruses. (Laboratory-confirmed deaths are thought to represent an undercount of the actual number. CDC has provided estimates about the number of 2009 H1N1 cases and related hospitalizations and deaths.
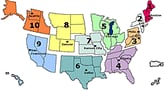
- One state (Alabama) continues to report widespread influenza activity; a decline of three states from last week. Twelve states continue to report regional influenza activity. They are: California, Georgia, Hawaii, Indiana, Maine, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Tennessee, and Virginia.
- Almost all of the influenza viruses identified so far continue to be 2009 H1N1 influenza A viruses. These viruses remain similar to the virus chosen for the 2009 H1N1 vaccine, and remain susceptible to the antiviral drugs oseltamivir and zanamivir with rare exception.
*All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
U.S. Situation Update
U.S. Patient Visits Reported for Influenza-like Illness (ILI)
U.S. Influenza-like Illness (ILI) Reported by Regions
|
Cases Defined by
|
Hospitalizations
|
Deaths
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza Laboratory-Tests** | 37,778 | 1,735 | |
|
*Reports can be based on syndromic, admission or discharge data, or a combination of data elements that could include laboratory-confirmed and influenza-like illness hospitalizations. *Laboratory confirmation includes any positive influenza test (rapid influenza tests, RT-PCR, DFA, IFA, or culture), whether or not typing was done. The table shows aggregate reports of all laboratory confirmed influenza hospitalizations and deaths (including 2009 H1N1 and seasonal flu) since August 30, 2009 received by CDC from U.S. states and territories**. This table will be updated weekly each Friday at 11 a.m. For the 2009-2010 influenza season, states are reporting based on new case definitions for hospitalizations and deaths effective August 30, 2009. CDC will continue to use its traditional surveillance systems to track the progress of the 2009-2010 influenza season. For more information about influenza surveillance, including reporting of influenza-associated hospitalizations and deaths, see Questions and Answers: Monitoring Influenza Activity, Including 2009 H1N1. The number of 2009 H1N1 hospitalizations and deaths reported to CDC from April – August 2009 is available on the Past Situation Updates page. For state level information, refer to state health departments. International Human Cases of 2009 H1N1 Flu Infection
**States report weekly to CDC either 1) laboratory-confirmed influenza hospitalizations and deaths or 2) pneumonia and influenza syndrome-based cases of hospitalization and death resulting from all types or subtypes of influenza. Although only the laboratory confirmed cases are included in this report, CDC continues to analyze data both from laboratory confirmed and syndromic hospitalizations and deaths. |
|||
|
Date Reported
|
Laboratory-Confirmed 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pediatric Deaths
|
Laboratory-Confirmed Influenza A Subtype Unknown Pediatric Deaths
|
Laboratory-Confirmed
Seasonal Influenza |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Week (Week 52, December 27, 2009 to January 2, 2010) | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Since August 30, 2009 | 188 | 40 | 1 | 229 |
| Cumulative since April 26, 2009 | 248 | 43 | 2 | 293 |
|
This table is based on data reported to CDC through the Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality Surveillance System. Influenza-associated deaths in children (persons less than 18 years) was added as nationally notifiable condition in 2004. For more information about influenza-associated pediatric mortality, see FluView. |
||||
For more information about the U.S. situation, see the CDC H1N1 Flu U.S. Situation page.
International Situation Update
 This report provides an update to the international situation as of January 4, 2010. The World Health Organization (WHO) continues to report laboratory-confirmed 2009 H1N1 flu cases and deaths on its
Web page. These laboratory-confirmed cases represent a substantial underestimation of total cases in the world, as most countries focus surveillance and laboratory testing only on people with severe illness. The 2009 H1N1 influenza virus continues to be the dominant influenza virus in circulation in the world. For the most recent period in which data are available, from December 13 to December 19, 2009, 87% of influenza specimens reported to WHO were 2009 H1N1, 0.2% were seasonal A (H1), 1.6%
were A (H3), 7.7% were influenza A viruses that were not subtyped, and 3.4% were influenza B viruses. In temperate regions of the Southern Hemisphere, sporadic cases of 2009 H1N1 continue to be reported but no sustained community transmission has been observed. In tropical regions of the Americas and Asia, influenza activity due to 2009 H1N1 remains variable. In temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, influenza-like illness (ILI) activity due to 2009 H1N1 has returned to baseline or below
baseline in North America. Overall, pandemic influenza activity appears to have peaked in most Western European countries but remains active in Central and Eastern European countries. In Western and Central Asia, influenza activity continues to persist above baseline levels.
This report provides an update to the international situation as of January 4, 2010. The World Health Organization (WHO) continues to report laboratory-confirmed 2009 H1N1 flu cases and deaths on its
Web page. These laboratory-confirmed cases represent a substantial underestimation of total cases in the world, as most countries focus surveillance and laboratory testing only on people with severe illness. The 2009 H1N1 influenza virus continues to be the dominant influenza virus in circulation in the world. For the most recent period in which data are available, from December 13 to December 19, 2009, 87% of influenza specimens reported to WHO were 2009 H1N1, 0.2% were seasonal A (H1), 1.6%
were A (H3), 7.7% were influenza A viruses that were not subtyped, and 3.4% were influenza B viruses. In temperate regions of the Southern Hemisphere, sporadic cases of 2009 H1N1 continue to be reported but no sustained community transmission has been observed. In tropical regions of the Americas and Asia, influenza activity due to 2009 H1N1 remains variable. In temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, influenza-like illness (ILI) activity due to 2009 H1N1 has returned to baseline or below
baseline in North America. Overall, pandemic influenza activity appears to have peaked in most Western European countries but remains active in Central and Eastern European countries. In Western and Central Asia, influenza activity continues to persist above baseline levels.
For more information about the international situation, see the CDC H1N1 Flu International Situation page.
CDC Experts Contributing to WebMD's Focus on Flu Blog
 In collaboration with WebMD, experts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are guest blogging and helping to answer
questions on WebMD's
Focus on Flu Blog. Check out the recent CDC blog post by Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH, medical epidemiologist with the CDC's Influenza Division -- Is H1N1 Gone?
In collaboration with WebMD, experts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are guest blogging and helping to answer
questions on WebMD's
Focus on Flu Blog. Check out the recent CDC blog post by Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH, medical epidemiologist with the CDC's Influenza Division -- Is H1N1 Gone?
Recent Updates of Interest
- UPDATE: 2009 H1N1 Flu International Situation Update
This report provides an update to the international situation as of January 8, 2010. The World Health Organization (WHO) continues to report updated 2009 H1N1 flu-associated laboratory-confirmed cases and deaths on its Web page. - UPDATE: Weekly FluView Map and Surveillance Report for Week Ending January 2, 2010
During week 52 (December 27, 2009-January 2, 2010), influenza activity decreased slightly in the U.S.161 (3.9%) specimens tested by U.S. World Health Organization (WHO) and National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System (NREVSS) collaborating laboratories and reported to CDC/Influenza Division were positive for influenza. - UPDATE: Influenza and Pneumonia-Associated Hospitalizations and Deaths from August 30, 2009 to January 2, 2010
Flu Activity: Overall flu activity in the United States decreased slightly during the week of December 27-January 2, 2010, as reported in FluView. Though flu activity, caused by either 2009 H1N1 or seasonal flu viruses, may rise and fall, it is expected to continue for several more months. Vaccination: CDC recommends influenza vaccination as the first and most important step in protecting against the flu. The week of January 10-16, 2010 marks this season’s National Influenza Vaccination Week (NIVW), a national observance to highlight the importance of continuing influenza vaccination beyond the holiday season. Because supplies of the 2009 H1N1 vaccines have increased dramatically, CDC is now encouraging everyone who has been patiently waiting to receive the 2009 H1N1 vaccine to get vaccinated at this time. - NEW: Flu information for People with Diabetes and Caregivers of People with Diabetes
People with diabetes are more likely to get flu-related complications like pneumonia and even be hospitalized or die from the flu than other people. Influenza may also interfere with blood glucose management. This fact sheet contains important information for diabetics. - NEW: Fact Sheet: Safety of Thimerosal in Vaccines Against 2009 H1N1 Flu
CDC is aware that pregnant women, parents of young children, and others may have questions about the safety of thimerosal in vaccines against 2009 H1N1 flu. The following fact sheet provides some information to help in making decisions.
Additional Updates on the CDC H1N1 Flu Website
To learn about other recent updates made to the CDC H1N1 Flu Website, please check the "What's New" page on the CDC H1N1 Flu website.
Get H1N1 Updates & Health Tips via Text Message
 Sign up to get health updates sent via text message. Messages are sent about three times a week with relevant H1N1 flu updates and timely health tips.
Sign up to get health updates sent via text message. Messages are sent about three times a week with relevant H1N1 flu updates and timely health tips.
Text UPDATES to 87000 to sign up.
To learn more, see www.cdc.gov/mobile.
Modify/Update Subscriber Preferences | Unsubscribe | Send Feedback | Learn more about CDC Email Updates
To receive the latest news for your region, please update your profile with your country, state and zip code.
Questions or problems? Please contact support@xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.

|
Fight Flu with Facts! • Visit Flu.gov
|

|
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) · 1600 Clifton Rd · Atlanta GA 30333 · 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636)

